Calculates absolute array norm, absolute difference norm, or relative difference norm
nrm = cv.norm(src1)
nrm = cv.norm(src1, src2)
nrm = cv.norm(..., 'OptionName', optionValue, ...)
Input
- src1 first input array.
- src2 second input array of the same size and the same type as
src1.
Output
- nrm the calculated norm.
Options
- NormType type of the norm, default 'L2'. One of:
- Inf Infinity norm (maximum norm).
- L1 L1 norm (Taxicab norm or Manhattan norm).
- L2 L2 norm (Euclidean norm).
- L2Sqr Squared L2 norm.
- Hamming In the case of one input array, calculates the Hamming distance of the array from zero. In the case of two input arrays, calculates the Hamming distance between the arrays.
- Hamming2 Similar to 'Hamming', but in the calculation, each two bits of the input sequence will be added and treated as a single bit to be used in the same calculation as 'Hamming'.
- Relative if true, computes relative difference, otherwise absolute difference. default false
- Mask optional operation mask; it must have the same size as
src1and logical type. Not set by default.
In the first variant (when there is no src2), the function cv.norm
calculates the absolute norm of src1. The type of norm to calculate is
specified using NormType:
{ ||src1||_Linf = max(abs(src1(:))) , if NormType='Inf'
norm = { ||src1||_L1 = sum(abs(src1(:))) , if NormType='L1'
{ ||src1||_L2 = sqrt(sum(src1(:).^2)) , if NormType='L2'
{ (||src1||_L2)^2 = sum(src1(:).^2) , if NormType='L2Sqr'
In the second variant, the function calculates the absolute difference norm
or the relative difference norm of arrays src1 and src2. The type of
norm to calculate is specified using NormType:
{ ||src1 - src2||_Linf = max(abs(src1(:) - src2(:))) , if NormType='Inf'
norm = { ||src1 - src2||_L1 = sum(abs(src1(:) - src2(:))) , if NormType='L1'
{ ||src1 - src2||_L2 = sqrt(sum((src1(:) - src2(:)).^2)) , if NormType='L2'
{ (||src1 - src2||_L2)^2 = sum((src1(:) - src2(:)).^2) , if NormType='L2Sqr'
or:
{ ||src1 - src2||_Linf / ||src2||_Linf , if NormType='Inf' && Relative=True
norm = { ||src1 - src2||_L1 / ||src2||_L1 , if NormType='L1' && Relative=True
{ ||src1 - src2||_L2 / ||src2||_L2 , if NormType='L2' && Relative=True
{ (||src1 - src2||_L2 / ||src2||_L2)^2 , if NormType='L2Sqr' && Relative=True
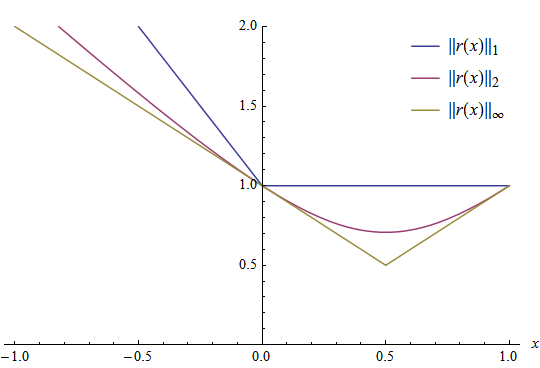
As example for one array consider the function r(x) = [x; 1-x],
x in [-1;1]. The L1, L2 and Linf norm for the sample value
r(-1) = [-1; 2] is calculated as follows:
||r(-1)||_L1 = abs(-1) + abs(2) = 3
||r(-1)||_L2 = sqrt((-1)^2 + (2)^2) = sqrt(5)
||r(-1)||_Linf = max(abs(-1), abs(2)) = 2
and for r(0.5) = [0.5; 0.5] the calculation is:
||r(0.5)||_L1 = |0.5| + |0.5| = 1
||r(0.5)||_L2 = sqrt((0.5)^2 + (0.5)^2) = sqrt(0.5)
||r(0.5)||_Linf = max(abs(0.5), abs(0.5)) = 0.5
The following graphic shows all values for the three norm functions
||r(x)||_L1, ||r(x)||_L2 and ||r(x)||_Linf.
It is notable that the L1 norm forms the upper and the Linf norm forms the
lower border for the example function r(x).
When the Mask parameter is specified and it is not empty, the norm is
calculated only over the region specified by the mask.
Multi-channel input arrays are treated as single-channel arrays, that is, the results for all channels are combined.
Hamming norms can only be calculated with uint8 depth arrays.